Introduction
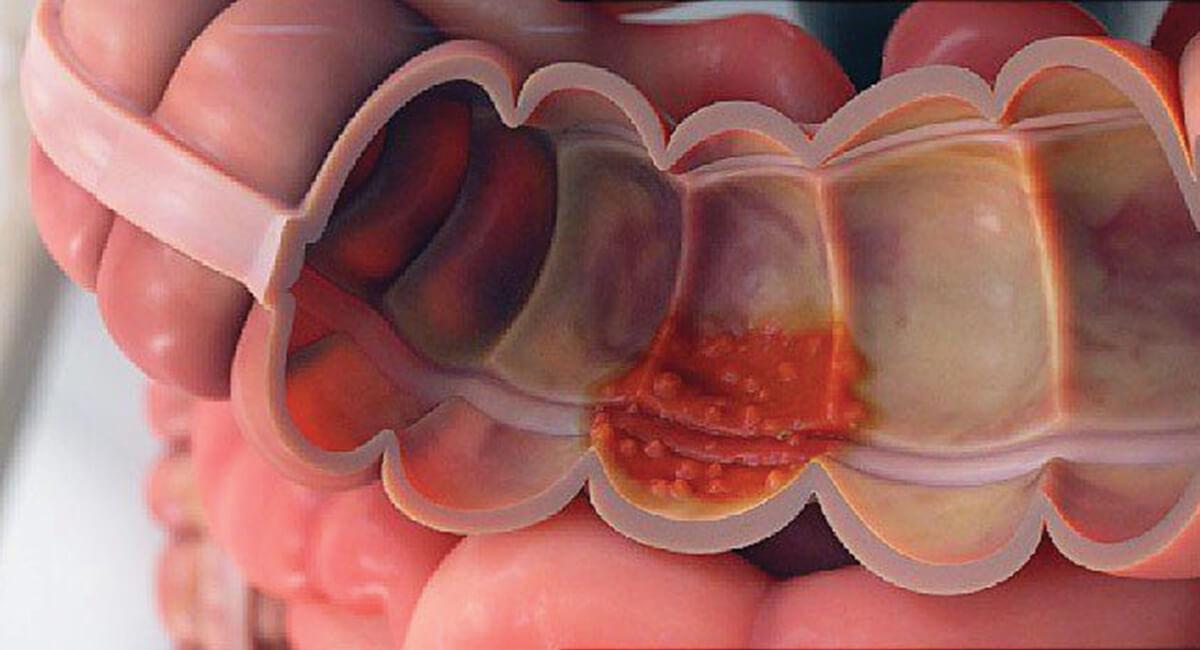
Ulcerative Colitis is a common inflammatory bowel disease responsible for inflammation and soreness of the gastrointestinal tract. There are mild to severe forms of Ulcerative Colitis that can be treated with proper medication and care. In some cases, the doctor may also recommend surgery.
Ulcerative Colitis causes inflammation and soreness in the linings of the large intestine. It is a common bowel disease with no cure. Ulcerative Colitis may cause inflammation in multiple parts of the body, such as joints, eyes, spine, and liver.
Request an Appointment at Smiles
What are the Causes of Ulcerative Colitis?
In Ulcerative Colitis, inflammation is caused by your immune system as it mistakes food, gut bacteria, and intestinal linings as intruders. Due to this, your white blood cells attack your intestinal lining, leading to inflammation.
The exact cause of Ulcerative Colitis is still unknown. However, some research suggests a link between genetics and the likelihood of developing Ulcerative Colitis (UC).
What are the Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis?
- ● Diarrhoea (sometimes with blood or pus)
- ● Pain or cramps in the abdomen
- ● Loss of appetite
- ● Dehydration
- ● Fever and fatigue
- ● Painful joints
- ● Painful eyes
- ● Skin sores
- ● Urge to empty your stomach
- ● Bleeding in stools
- ● Fatigue
- ● Anaemia
- ● Malnutrition
- ● Weight loss
- ● Skin problems
- ● Pain in the rectal area
- ● Nausea
- ● Night sweats
The signs and symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis may flare up with some triggers. Ulcerative colitis may be recurrent.
How is Ulcerative Colitis Diagnosed?
- Blood tests: Blood tests help in the diagnosis of Ulcerative Colitis and anaemia.
- Stool sample test: A stool test helps rule out the possibility of parasites that may resemble Ulcerative Colitis. It also confirms the presence of blood in your stools.
- Colonoscopy: This diagnostic method involves inserting a thin tube into your rectum with a camera attached to one end. It allows the doctor to examine the insides of your colon to give a proper diagnosis.
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy: This technique is similar to colonoscopy. It involves using a flexible tube that may also be used to collect samples of colon tissue for biopsy.
If you have severe Ulcerative Colitis, the doctor may ask for scan tests such as:
- CT-Scan: A CT scan of your colon and abdomen can help the doctor understand the severity of ulcerative colitis. It is also useful in diagnosing complications caused by Ulcerative Colitis.
- X-ray: In case of severe symptoms, the doctor may suggest an x-ray to rule out the possibility of other life-threatening conditions. A barium enema is used for the diagnosis of Ulcerative Colitis.
How is Ulcerative Colitis Treated?
- Medications
- ● Anti-diarrhoea medicines: Diarrhea is a common symptom of ulcerative colitis (UC). It may lead to water loss from the body and cause fatigue. The doctor will recommend medicines to treat diarrhoea.
- ●Pain-relieving medicines: This bowel disease is known for causing mild to severe intensity cramps and abdominal pain. Depending upon the severity of your pain, the doctor will recommend the right pain killer. In the case of cramps, the doctor may also prescribe antispasmodic medicines to soothe discomfort.
- ● Iron supplements: In many cases, anaemia is found among patients who suffer from the condition of ulcerative colitis. You will need to take a daily dose of iron supplements to deal with this condition. The right amount of iron in the body can help increase oxygen levels in your blood.
- ● Anti-inflammatory drugs: The use of anti-inflammatory drugs like corticosteroids can reduce inflammation in your body.
- ● 5-ASA compounds: Acetylsalicylic acid helps in reducing inflammation near the rectal area.
- Surgery
If your body does not respond well to the prescribed medicines, the doctor may recommend surgery. Surgery is also considered as one of the treatment options in case of severe symptoms.
With surgery, a part of your colon may be removed, and a pathway is created for easy excretion of waste. In most cases, J pouch surgery is conducted.
- Lifestyle
The symptoms of ulcerative colitis flare-up with some known triggers. Lifestyle changes can be useful in managing symptoms and discomfort. Some specific foods and beverages are known to trigger ulcerative colitis. Dietary changes eliminating the same can prove beneficial in managing ulcerative colitis.
- ● Limit your alcohol, caffeine, and dairy consumption. In many cases, dairy consumption makes UC worse due to the presence of lactose.
- ● Increase your water intake
- ● Take smaller meals
- ● Exercise daily to maintain overall health and reduce stress
- ● Practice relaxation techniques
What is the Results of Ulcerative Colitis Treatment?
What are the Risks Associated with Ulcerative Colitis treatments?
- ● After surgery, you may experience more frequent and watery bowel movements.
- ● Allergic reaction
- ● Anaesthesia-related complications
- ● Breathing issues
- ● Bleeding
- ● Blood clots
- ● Risks of catching an infection
Conclusion
Ulcerative Colitis surgery may cause health complications such as nerve damage, intestinal scars, damage to internal organs and blockage of the intestines also.
Ulcerative Colitis
Request an Appointment at Smiles
FAQ's
Can Ulcerative Colitis Lead to Colon Cancer?
Is Surgery Recommended in Mild Cases of Ulcerative Colitis?
Can Antibiotics Improve Symptoms of UC?
Need Help?
For any Information about our Locations, Doctors or Treatments.
