Introduction
The fast lifestyle that we are leading these days has aggravated many diseases. The tendency to eat more junk food has dramatically increased disorders related to the digestive system.
The propensity to eat fast owing to a speedy lifestyle has created many health-related problems such as indigestion and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease.
Although Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease is a chronic disease, it is aggravated by an unhealthy lifestyle, especially one involving unhealthy eating habits.
Request an Appointment at Smiles
What is Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease?
Acid reflux is a common phenomenon and can occur in all human beings as many as two times a week. But when acid reflux increases in occurrence, it is called gastroesophageal reflux disease or GERD.
GERD is mostly treated with over-the-counter medicines and specific lifestyle changes. But in some severe cases, GERD may also require surgery or more potent medication prescribed by your gastroenterologist.
What are the Causes of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease?
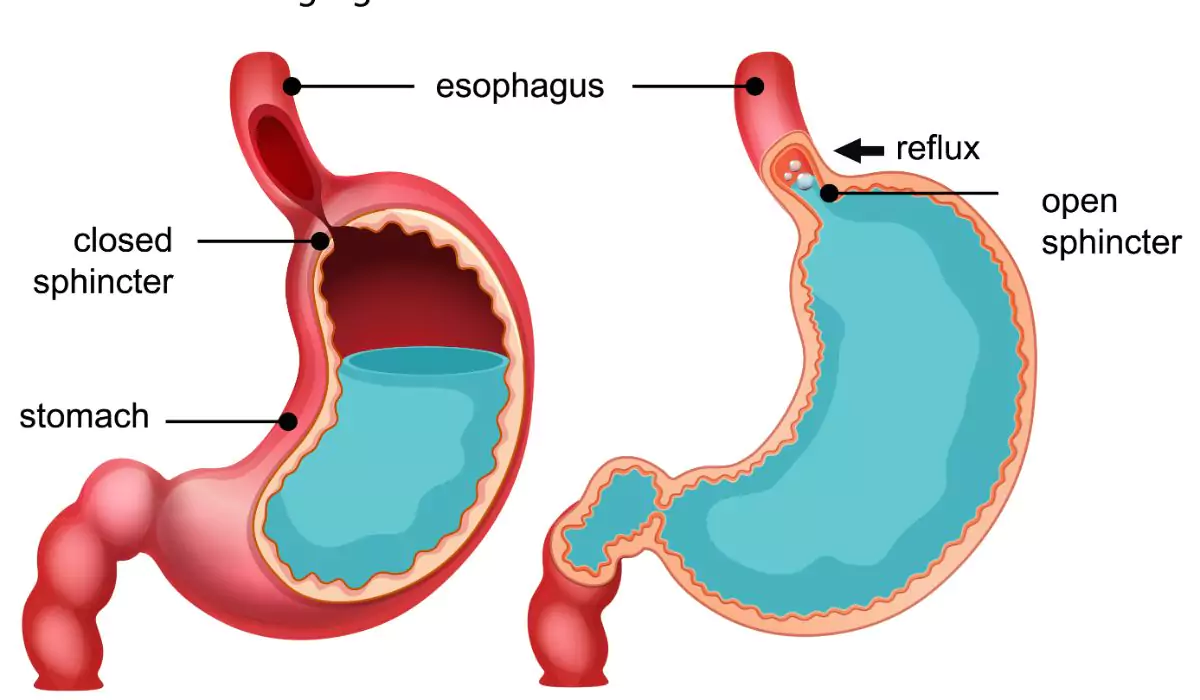
When you swallow your food, a circular band of muscle around the lower portion of your oesophagus, called the lower oesophagal sphincter, relaxes and allows the swallowed particle to move into your stomach.
After this process, your sphincter will close. If your sphincter becomes weak, then the acids in your stomach will flow back to your oesophagus.
When your oesophagus is continuously irritated by stomach acids, it becomes inflamed, leading to Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Certain lifestyle disorders can aggravate GERD:
- ● Smoking
- ● Eating junk, fried food
- ● Drinking beverages such as coffee and alcohol
- ● Unhealthy lifestyle such as eating late at night and indulging in large meals
- ● Consuming medicines such as Aspirin on a daily basis
Certain factors can increase your risk of GERD, among which are:
- ● Hiatal hernia, which causes the top of the stomach to bulge into the diaphragm
- ● Obesity
- ● Pregnancy
- ● Scleroderma, which is a disorder of the connective tissues
- ● The tendency to keep the stomach empty for long hours
What Are the Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease?
- ● Heartburn, especially after eating, and it deteriorates at night. Lying down or bending can worsen the burning sensation. Standing may help ease the heartburn because the acid moves back to the stomach.
- ● Chest pain
- ● Difficulty in swallowing
- ● A feeling of a lump in the throat
- ● Nausea and vomiting
- ● Bad breath
- ● The tooth enamel wears away.
- ● Breathing trouble
The following symptoms may accompany acid reflux at night:
- ● Persistent cough
- ● Laryngitis (inflammation of the larynx)
- ● Sudden onset of asthma
- ● Problems in sleep
How is Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Diagnosed?
- ● Ambulatory acid (pH) probe test: In this test, a monitor is put in your oesophagus to check for how long the stomach acids stay there. The monitor is connected to a small computer that is attached either to your waist or shoulder.
The monitor is either a thin tube passed through your nose to the oesophagus or a clip placed in your oesophagus through an endoscopic device. The clip will pass out through your stool in two or three days.
- ● Upper endoscopy: In this test, your doctor will insert a light and camera attached to a flexible and narrow tube down your throat to check the oesophagus and stomach.
An endoscopy is used to detect inflammation in the oesophagus or to collect tissue samples for biopsy. A biopsy is conducted to check for Barrett’s oesophagus.
- ● X-ray of the upper digestive system: Before conducting your x-ray, your doctor makes you drink a chalky liquid that will adhere to the inner lining of the digestive tract. The liquid provides a better view of the stomach, oesophagus and upper intestine.
- ● Oesophagal manometry: This test is conducted to measure your oesophagus’ muscle contractions when you swallow something.
How is Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Treated?
- ● Over the counter medicines: Antacids such as Mylanta and Tums can provide quick relief from stomach acid.
H-2 receptor blockers such as famotidine and nizatidine, provide long term relief and decrease acid production. Proton pump inhibitors like omeprazole and lansoprazole are strong acid blockers.
- ● Prescription medicines: Prescription medicines to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease include famotidine and nizatidine. Prescription-strength proton pump inhibitors include esomeprazole, pantoprazole, rabeprazole and dexlansoprazole.
- ● Surgery and other procedures: If medicines cannot control GERD, your doctor might suggest surgery. Surgery includes fundoplication, implantation of LYNX device and transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF).
What is the Results of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Treatment?
In fundoplication, the top of the stomach is wrapped around the lower oesophagal sphincter to prevent acid reflux. The LINX device’s implantation also helps close the oesophagus and stomach junction to avoid acid reflux.
Transoral incisionless fundoplication or TIF helps in quick recovery because it is incision-less. The lower oesophagal sphincter is partially wrapped around the lower oesophagus. The procedure is done through the mouth using an endoscope.
What are the Risks Associated with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease treatments?
Request an Appointment at Smiles
FAQ's
How Long does it take to Recover from GERD?
Can GERD be Cured Permanently?
Is GERD a Lifelong Disease?
What Foods should you Avoid when you’re Diagnosed with GERD?
Is Coffee Bad for GERD?
What Food is Good for GERD?
Need Help?
For any Information about our Locations, Doctors or Treatments.
